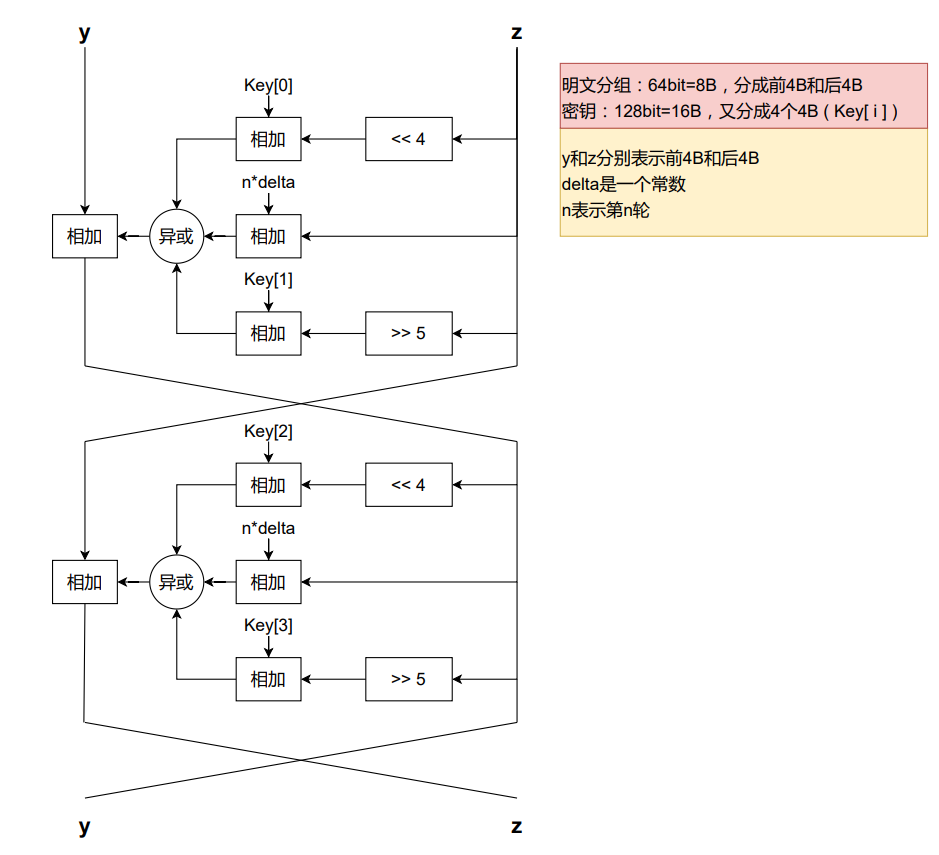
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
import bitarray as ba
from bitarray.util import ba2int, int2ba, hex2ba
from ctypes import c_uint32
class TEA:
def __init__(self, key: bytes):
key = self.pad(key, max_len=16)
self.key = [ba2int(hex2ba(key[i * 4:i * 4 + 4].hex())) for i in range(4)]
self.delta = 0x9E3779B9
@staticmethod
def pad(x: bytes, max_len=8):
"""
RFC 5652 #6.3 PKCS#7 Padding
example: 7F [] [] [] [] [] [] [] -> 7F 07 07 07 07 07 07 07
81 F1 B2 1C [] [] [] [] -> 81 F1 B2 1C 04 04 04 04
"""
pad_len = max_len - len(x) % max_len
hex_len = hex(pad_len)[2:]
if len(hex_len) % 2 != 0:
hex_len = "0" + hex_len
return x if pad_len == max_len else x + pad_len * bytes.fromhex(hex_len)
@staticmethod
def unpad(x: bytes):
"""
Detect Padding
"""
item = x.hex()[-2:]
if item not in ['01', '02', '03', '04', '05', '06', '07']:
return x
item_num = int(item)
if not x[-item_num:].hex() == item * item_num:
return x
return x[:-item_num]
def encrypt(self, data: bytes):
data = self.pad(data)
res = ba.bitarray()
for i in range(len(data) // 8):
delta_sum = c_uint32(0)
plaintext = ba.bitarray()
plaintext.frombytes(data[i * 8:(i + 1) * 8])
y, z = c_uint32(ba2int(plaintext[:32])), c_uint32(ba2int(plaintext[32:]))
for n in range(32):
delta_sum.value += self.delta
y.value += ((z.value << 4) + self.key[0]) ^ (z.value + delta_sum.value) ^ ((z.value >> 5) + self.key[1])
z.value += ((y.value << 4) + self.key[2]) ^ (y.value + delta_sum.value) ^ ((y.value >> 5) + self.key[3])
res += int2ba(y.value, 32) + int2ba(z.value, 32)
return res.tobytes().hex()
def decrypt(self, data: bytes):
res = ba.bitarray()
for i in range(len(data) // 8):
delta_sum = c_uint32(0xC6EF3720)
ciphertext = ba.bitarray()
ciphertext.frombytes(data[i * 8:(i + 1) * 8])
y, z = c_uint32(ba2int(ciphertext[:32])), c_uint32(ba2int(ciphertext[32:]))
for n in range(32):
z.value -= ((y.value << 4) + self.key[2]) ^ (y.value + delta_sum.value) ^ ((y.value >> 5) + self.key[3])
y.value -= ((z.value << 4) + self.key[0]) ^ (z.value + delta_sum.value) ^ ((z.value >> 5) + self.key[1])
delta_sum.value -= self.delta
res += int2ba(y.value, 32) + int2ba(z.value, 32)
return self.unpad(res.tobytes())
tea = TEA(b'123456')
cipher_text = tea.encrypt(b'Hello World!')
print(cipher_text)
plain_text = tea.decrypt(bytes.fromhex(cipher_text))
print(plain_text)
|